Note: This tutorial assumes that Node.js is already installed on your computer. If it's not, you'll need to install it first from nodejs.org before proceeding.
👉 This setup allows real-time communication between the browser and server.
WebSocket Server (Node.js with ws library)
First, we'll create a basic WebSocket echo server written in Node.js using ws library. It listens for incoming connections, receives messages from clients, and sends them back (echoes them).
Follow these steps.
1) Press window + R buttons to open the run window. Type cmd and hit the Enter button to open the "command" window.
2) Run node -v to check the current version of "Node.js".
3) Create a new folder where you want to run the project. For example, mkdir MyNewFolder. Navagate (or move) to the newly created folder: cd C:\Users\YourUsername\MyNewFolder.
4) Inside the folder create a file named server.js. Write the below code inside the file.
const WebSocket = require('ws'); const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ port: 8080 }); wss.on('connection', function connection(ws) { console.log('Client connected'); ws.on('message', function incoming(message) { console.log('Received:', message); ws.send(`Echo: ${message}`); }); ws.on('close', () => { console.log('Client disconnected'); }); });
Your server is ready. To run this first install ws package from the command window.
npm install ws
Next, start the server.
node server.js
👉 You can close the server by using CTRL + C buttons.
What this Code does?
const WebSocket = require('ws'); - This imports the ws (the WebSocket) module, which provides WebSocket functionality in "Node.js". You must install it first using npm install ws.
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ port: 8080 }); - It creates new WebSocket that listens on port 8080. The constant variable "wss" stands for "WebSocket Server".
wss.on('connection', function connection(ws) { - This code sets up an event listener for when a client connects to the server. The The "ws" object represents the individual client’s WebSocket connection.
ws.on('message', function incoming(message) { - Here, it listens for messages sent by the client (the browser app). The message parameter contains the data the client sends.
ws.send(`Echo: ${message}`); - This code sends a response back to the client, echoing the message with a prefix.
ws.on('close', () => {...}); - It listens for when the client disconnects and logs the event to the console.
The Client Application
Now let's create the client application using JavaScript and HTML.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>WebSocket Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>WebSocket Client</h2>
<input type="text" id="msgInput" placeholder="Type a message">
<button onclick="sendMessage()">Send</button>
<div id="output"></div>
<script>
const socket = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:8080');
socket.onopen = () => {
document.getElementById('output').innerText += 'Connected to server\n';
};
socket.onmessage = (event) => {
document.getElementById('output').innerText += `Server: ${event.data}\n`;
};
socket.onclose = () => {
document.getElementById('output').innerText += 'Disconnected from server\n';
};
function sendMessage() {
const msg = document.getElementById('msgInput').value;
socket.send(msg);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Real time communication between the browser and server.
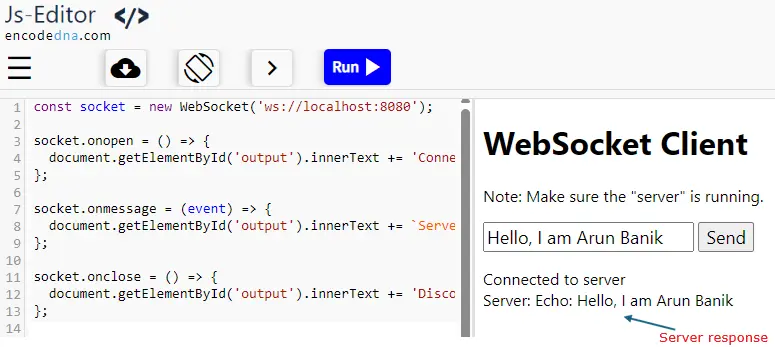
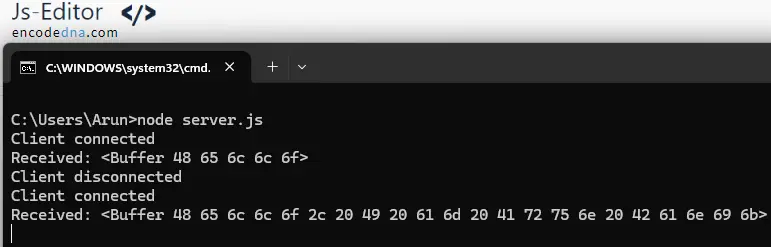
👉 This example sets up a basic echo server. So, whatever message you send from the client gets echoed back by the server.
🚀 If you've already explored this Node.js WebSocket example, you might enjoy seeing it in action through a simple jQuery based chat application, a great way to visualize real-time communication in a browser friendly setup.
