But what if there were a cleaner, more responsive way to achieve the same result, without relying on absolute positioning at all? Enter Flexbox, CSS's modern layout engine that makes top-right alignment not just possible, but effortless. In this follow-up, we’ll explore how Flexbox can replicate and even improve upon the layout, offering better scalability, responsiveness, and control.
➡️ The flexbox property is best described here
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Flexbox Top-Right Menu</title>
<style>
* { font-family: 'Segoe UI', sans-serif; }
.parent {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
background: #CCFF33;
padding: 0;
height: auto;
overflow: hidden;
}
.top-bar {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
}
.menu {
background: #CC0000;
color: white;
padding: 5px 10px;
}
.content, p {
background: #0099FF;
color: #fff;
padding: 5px 10px;
text-align: center;
width: auto;
margin: 10px;
}
p {
background: transparent;
text-align: left;
color: #000;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="parent">
<div class="top-bar">
<div class="menu">MENU</div>
</div>
<p>This is the first element.</p>
<p>This is the second element.</p>
<div class="content">This is the third element.</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output:
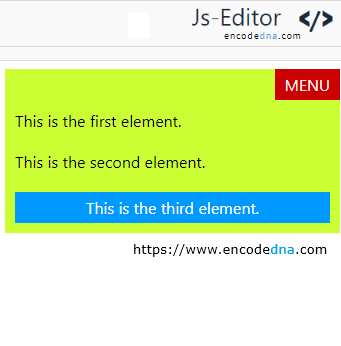
With Flexbox, there's no need to calculate pixel offset like top: 0 or right: 0.
The MENU element appears neatly in the top-right corner of the layout, thanks to Flexbox. No position: absolute, no float: right, just clean, modern CSS.
