In this tutorial you will learn how to,
📖 Read Excel data directly from a WinForms application
🖋️ Edit existing cells and modify spreadsheet content
➕ Add new records to an Excel file using C# code in WinForms
👉 Check this article if you are VB.NET developer.
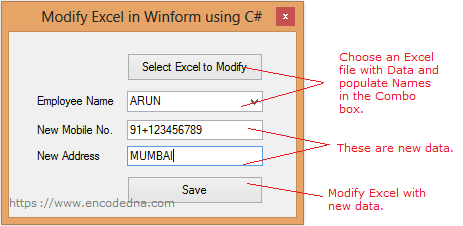
Scenario:
Here’s a simple scenario. I have an Excel file with employee details. It looks like this.
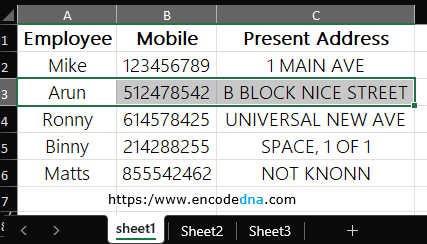
I'll select the Excel file from my WinForm application, extract "employee names" (only) and populate a Combo box. It will allow me to select the employee "name" whose phone no. and address I can change.
First, you’ll need to add COM library to your project. In your .Net IDE, click the "Project' tab from the top menu and choose Add Reference… In the Add Reference window, choose the "COM" tab. Find Microsoft Excel 12.0 Object Library (or any other version) from the list. Click Ok.
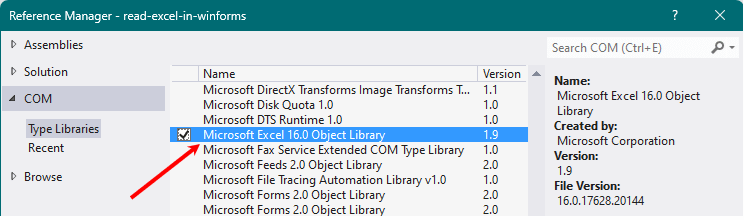
You now have access to the Interop namespace, which provides the necessary methods and properties to access Excel and the Microsoft Office apps.
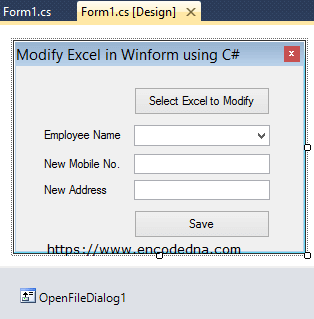
Create a C# project and add few controls to the form. Add have two buttons, a combo box and two textboxes. You can add labels too. In addition, add OpenFileDialog (to select files) control to the form.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Windows.Forms; using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel; // EXCEL APPLICATION. namespace edit_modify_excel { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } // CREATE EXCEL OBJECTS. Excel.Application xlApp = new Excel.Application(); Excel.Workbook xlWorkBook; Excel.Worksheet xlWorkSheet; string sFileName; int iRow, iCol = 2; // OPEN AND SELECT THE EXCEL FILE TO EDIT. private void cmdSelect_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { OpenFileDialog1.Title = "Excel File to Edit"; OpenFileDialog1.FileName = ""; OpenFileDialog1.Filter = "Excel File|*.xlsx;*.xls"; if (OpenFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { sFileName = OpenFileDialog1.FileName; if (sFileName.Trim() != "") { readExcel(sFileName); // READ EXCEL DATA. } } } // GET NAMES FROM EXCEL AND POPULATE COMB0 BOX. private void readExcel(string sFile) { xlApp = new Excel.Application(); xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(sFile); xlWorkSheet = xlWorkBook.Worksheets["Sheet1"]; // NAME OF THE SHEET. // START FROM THE SECOND ROW. for (iRow = 2; iRow <= xlWorkSheet.Rows.Count; iRow++) { if (xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value == null) { break; // BREAK LOOP. } else { // POPULATE COMBO BOX. cmbEmp.Items.Add(xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value); } } xlWorkBook.Close(); xlApp.Quit(); } private void cmdSave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (sFileName.Trim() != "") { modifyExcel(sFileName); // MODIFY DETAILS IN THE FILE. } } // NOW, MODIFY EMPLOYEE DETAILS WITH NEW DETAILS IN THE EXCEL FILE. private void modifyExcel(string sFile) { xlApp = new Excel.Application(); xlWorkBook = xlApp.Workbooks.Open(sFile); xlWorkSheet = xlWorkBook.Worksheets["Sheet1"]; // NAME OF THE SHEET. for (iRow = 2; iRow <= xlWorkSheet.Rows.Count; iRow++) // START FROM THE SECOND ROW. { if (xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value == null) { break; // BREAK, IF IT REACHED THE LAST ROW. } if (xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, 1].value == cmbEmp.Text) { xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, iCol].value = tbMobile.Text; // MODIFY MOBILE (IN CELL 2). xlWorkSheet.Cells[iRow, iCol + 1].value = tbAddress.Text; // MODIFY ADDRESS (IN CELL 3). } } xlWorkBook.Close(); xlApp.Quit(); // CLEAN UP. System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlApp); System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkBook); System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(xlWorkSheet); } } }
It’s a very simple code. I have two private methods named readExcel and modifyExcel. Both the methods take a parameter each, in the form of a "file name".
The first method "readExcel" is called after you select the Excel file. Here, it will extract all the Employee names in the "first" column and populate the Combo box with names.
The Second method "modifyExcel" will modify the phone number and address of the selected employee.
