💡 Think of map() like a magic copier. It goes through each item in your list, does something to it, and gives you a brand-new list with the results.
Syntax of map() function
array.map (function callback)
The map() function in JavaScript lets you loop through an array and apply a function to each item. This function is called a callback, takes the current item, does something with it, and returns a new value. All these returned values are collected into a brand-new array, leaving the original one unchanged.
In the first example, I have an array of code and each code is an "alpha-numeric" value. I want to extract only the text values (alphabets) and create a new array out of it.
<html>
<head>
<title>ES6 map() function Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Get only text from array using map()</h2>
<p id="msg"></p>
</body>
<script>
const arrCode = ['a1', 'c21', 'b9', 'cq87', 'qi8'];
// Extract only the text (non-digit characters) from each string.
const getOnlyText = val => val.match(/\D+/g)?.join('') || '';
// Use map to apply the function to each item in the array.
const textOnlyArray = arrCode.map(getOnlyText);
// Display the result in a readable format.
const msg = document.getElementById('msg');
msg.innerHTML = textOnlyArray.join(', ');
</script>
</html>In the example above, the callback function getOnlyText() receives each item from the array arrCode[] as its input. The map() method goes through the array one element at a time, passing each value to the callback. The function processes the value and returns only the text portion (i.e., the non-numeric characters). These returned results are then collected into a new array created by "map()".
Note: The "map()" method internally loops through each element of an array and applies a callback function to it. It's a cleaner alternative to using traditional loops like for, for...of, or even forEach() when your goal is to transform each item and return a new array of results.
🚀 Quick Tip:
• Use map() when you want to change each item.
• Use forEach() when you want to do something with each item (but don’t need a new array).
In-addition, see how I have used ES6’s arrow function (=>). The arrow function is another key feature, which was introduced in ES6.
const getOnlyText = (val) => { }
In this second example, I am using the map() function against a JSON array, to create a new array. The JSON has three objects, the id, name and type of birds.
Using the map() I can filter out the elements of my choice from the array.
<html>
<body>
<p id="msg"></p>
</body>
<script>
const birds = [
{"ID": "DV8", "Name": "Eurasian Collared-Dove", "Type": "Dove" },
{"ID": "HK12", "Name": "Bald Eagle", "Type": "Hawk" },
{"ID": "HK6", "Name": "Cooper's Hawk", "Type": "Hawk" },
{"ID": "SP11", "Name": "Bell's Sparrow", "Type": "Sparrow" },
{"ID": "DV2", "Name": "Mourning Dove", "Type": "Dove" }
];
const arrBirdID = birds.map(bird => bird.ID); // Or, simply use bird.Name to get the values from the "Name" object in the JSON array.
document.getElementById('msg').innerHTML = arrBirdID;
</script>
</html>Take a look at how I've used the map() function in this example. It's a great way to transform array elements. I've also used the arrow function (=>) to keep the code clean and concise.
This one-liner is a streamlined alternative to the longer method shown above. It achieves the same result with cleaner code.
const bird = (val) => {
return val.ID;
}
const arrBirdID = birds.map(bird);👇 Now try this ...
You can use multiple map() functions in a single statment. For example,
const arrBirdID = birds.map(bird => bird.ID).map(lc => lc.toLowerCase()); console.log(arrBirdID);
It's like telling JavaScript: "Go through all the IDs and convert each one to lowercase.". You can see the result at the bottom of the image.
image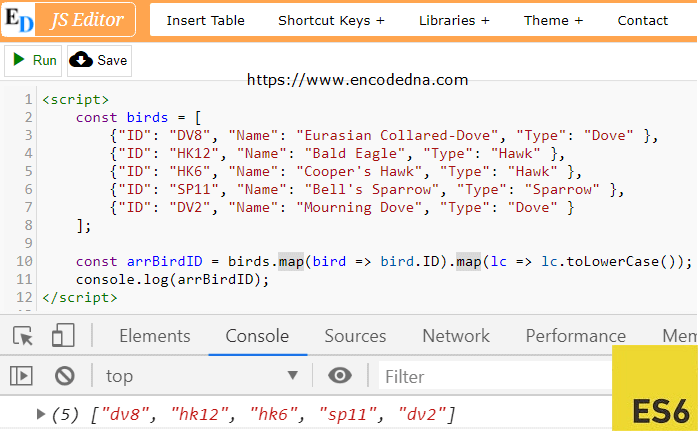
Here’s another example.
<script>
const numbers = [56, 12, 64, 22, 88];
const square = (val) => {
return Math.sqrt(val).toFixed(2);
}
const mapSquareRoot = numbers.map(square);
console.log(mapSquareRoot);
// OR SIMPLY USE ...
// const numbers = [56, 12, 64, 22, 88];
// const mapSquareRoot = numbers.map(num => Math.sqrt(num).toFixed(2));
// console.log(mapSquareRoot); 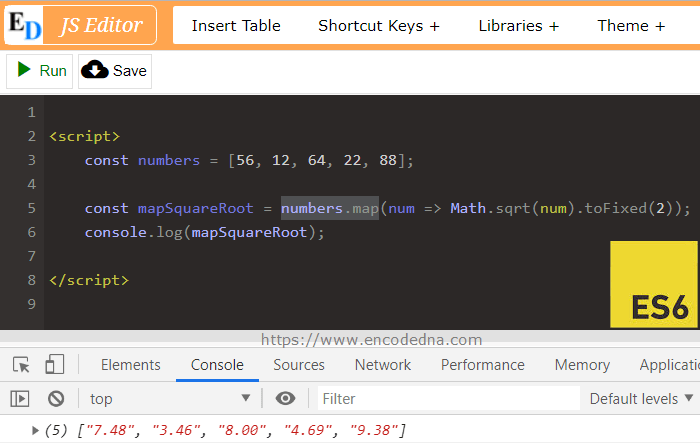
In the example above, the "map()" function generates a new array by applying the Math.sqrt() method to each number in the original array. This built-in method calculates the square root of a number, and "map()" makes it easy to apply it to every element in one clean step.
The map() function is a powerful alternative to traditional for loops, helping you write cleaner and more concise code. With just a bit of practice, it becomes second nature. I've picked up some handy tricks using this versatile ES6 feature, and now, so have you!
🚀 Bonus tip: You can even chain multiple map() calls in a single statement to perform complex transformations step by step. It’s a great way to keep your code readable and efficient.
